24. Application
Gtk.Application abrange muitas tarefas repetitivas que um aplicativo moderno precisa, como manipular várias instâncias, ativação do D-Bus, abertura de arquivos, análise de linha de comando, inicialização/desligamento, gerenciamento de menus, gerenciamento de janelas e muito mais.
24.1. Ações
Gio.Action é uma maneira de expor qualquer tarefa que seu aplicativo ou widget fizer por um nome. Essas ações podem ser desabilitadas/habilitadas no tempo de execução e podem ser ativadas ou ter um estado alterado (se elas contiverem estado).
O motivo para usar ações é separar a lógica da interface do usuário. Por exemplo, isso permite usar uma barra de menu no OSX e um menu de engrenagem no GNOME, simplesmente referenciando o nome de uma ação. A principal implementação que você estará usando é Gio.SimpleAction que será mostrado mais tarde.
Muitas classes, como Gio.MenuItem e Gtk.ModelButton suportam propriedades para definir um nome de ação.
Estas ações podem ser agrupadas em um Gio.ActionGroup e quando esses grupos são adicionados a um widget com Gtk.Widget.insert_action_group(), eles ganharão um prefixo. Tal como “win” quando adicionado a um Gtk.ApplicationWindow. Você usará o nome completo da ação ao fazer referência a ele, como “app.about”, mas ao criar a ação, ela ficará “about” até ser adicionada ao aplicativo.
Você também pode facilmente criar keybindings para ações definindo a propriedade accel no arquivo Gio.Menu ou usando Gtk.Application.set_accels_for_action().
24.3. Linha de comando
Ao criar seu aplicativo, ele recebe uma propriedade de flag de Gio.ApplicationFlags. Usando isso, você pode permitir que ele manipule tudo sozinho ou tenha um comportamento mais personalizado.
Você pode usar o HANDLES_COMMAND_LINE para permitir um comportamento customizado em Gio.Application.do_command_line(). Em combinação com Gio.Application.add_main_option() para adicionar opções personalizadas.
Usar HANDLES_OPEN fará o trabalho de simplesmente pegar argumentos de arquivo para você e permitir que você os manipule em Gio.Application.do_open().
Se o seu aplicativo já estiver aberto, todos serão enviados para a instância existente, a menos que você use NON_UNIQUE para permitir várias instâncias.
24.4. Exemplo
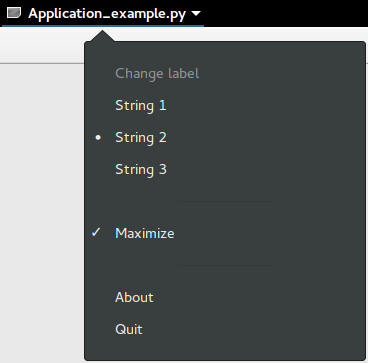
1import sys
2
3import gi
4
5gi.require_version("Gtk", "3.0")
6from gi.repository import GLib, Gio, Gtk
7
8# This would typically be its own file
9MENU_XML = """
10<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
11<interface>
12 <menu id="app-menu">
13 <section>
14 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">Change label</attribute>
15 <item>
16 <attribute name="action">win.change_label</attribute>
17 <attribute name="target">String 1</attribute>
18 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">String 1</attribute>
19 </item>
20 <item>
21 <attribute name="action">win.change_label</attribute>
22 <attribute name="target">String 2</attribute>
23 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">String 2</attribute>
24 </item>
25 <item>
26 <attribute name="action">win.change_label</attribute>
27 <attribute name="target">String 3</attribute>
28 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">String 3</attribute>
29 </item>
30 </section>
31 <section>
32 <item>
33 <attribute name="action">win.maximize</attribute>
34 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">Maximize</attribute>
35 </item>
36 </section>
37 <section>
38 <item>
39 <attribute name="action">app.about</attribute>
40 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">_About</attribute>
41 </item>
42 <item>
43 <attribute name="action">app.quit</attribute>
44 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">_Quit</attribute>
45 <attribute name="accel"><Primary>q</attribute>
46 </item>
47 </section>
48 </menu>
49</interface>
50"""
51
52
53class AppWindow(Gtk.ApplicationWindow):
54 def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
55 super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
56
57 # This will be in the windows group and have the "win" prefix
58 max_action = Gio.SimpleAction.new_stateful(
59 "maximize", None, GLib.Variant.new_boolean(False)
60 )
61 max_action.connect("change-state", self.on_maximize_toggle)
62 self.add_action(max_action)
63
64 # Keep it in sync with the actual state
65 self.connect(
66 "notify::is-maximized",
67 lambda obj, pspec: max_action.set_state(
68 GLib.Variant.new_boolean(obj.props.is_maximized)
69 ),
70 )
71
72 lbl_variant = GLib.Variant.new_string("String 1")
73 lbl_action = Gio.SimpleAction.new_stateful(
74 "change_label", lbl_variant.get_type(), lbl_variant
75 )
76 lbl_action.connect("change-state", self.on_change_label_state)
77 self.add_action(lbl_action)
78
79 self.label = Gtk.Label(label=lbl_variant.get_string(), margin=30)
80 self.add(self.label)
81 self.label.show()
82
83 def on_change_label_state(self, action, value):
84 action.set_state(value)
85 self.label.set_text(value.get_string())
86
87 def on_maximize_toggle(self, action, value):
88 action.set_state(value)
89 if value.get_boolean():
90 self.maximize()
91 else:
92 self.unmaximize()
93
94
95class Application(Gtk.Application):
96 def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
97 super().__init__(
98 *args,
99 application_id="org.example.myapp",
100 flags=Gio.ApplicationFlags.HANDLES_COMMAND_LINE,
101 **kwargs
102 )
103 self.window = None
104
105 self.add_main_option(
106 "test",
107 ord("t"),
108 GLib.OptionFlags.NONE,
109 GLib.OptionArg.NONE,
110 "Command line test",
111 None,
112 )
113
114 def do_startup(self):
115 Gtk.Application.do_startup(self)
116
117 action = Gio.SimpleAction.new("about", None)
118 action.connect("activate", self.on_about)
119 self.add_action(action)
120
121 action = Gio.SimpleAction.new("quit", None)
122 action.connect("activate", self.on_quit)
123 self.add_action(action)
124
125 builder = Gtk.Builder.new_from_string(MENU_XML, -1)
126 self.set_app_menu(builder.get_object("app-menu"))
127
128 def do_activate(self):
129 # We only allow a single window and raise any existing ones
130 if not self.window:
131 # Windows are associated with the application
132 # when the last one is closed the application shuts down
133 self.window = AppWindow(application=self, title="Main Window")
134
135 self.window.present()
136
137 def do_command_line(self, command_line):
138 options = command_line.get_options_dict()
139 # convert GVariantDict -> GVariant -> dict
140 options = options.end().unpack()
141
142 if "test" in options:
143 # This is printed on the main instance
144 print("Test argument recieved: %s" % options["test"])
145
146 self.activate()
147 return 0
148
149 def on_about(self, action, param):
150 about_dialog = Gtk.AboutDialog(transient_for=self.window, modal=True)
151 about_dialog.present()
152
153 def on_quit(self, action, param):
154 self.quit()
155
156
157if __name__ == "__main__":
158 app = Application()
159 app.run(sys.argv)